高考试题
A. 西汉的“内朝”
B. 唐宋的政事堂
C. 明朝的内阁
D. 清朝的军机处
A. 监督国家机关及其工作人员的关键
B. 我国公民享有的最基本的民主权利
C. 实现中国
 的领导的重要方式
的领导的重要方式
材料一:下图是2016-2018年我国减税数额和税收年增长率

(1)分析上图所包含的经济信息。
材料二:2018年12月25日,我国发布《市场准入负面清单(2018年版)》,全面实施市场准入负面清单制度。清单以外的行业、领域、业务等,各类市场主体皆可依法平等进入,实现“非禁即入”。与此同时,我国还陆续推出一系列针对小微企业的普惠性减税措施,大幅放宽可享受企业所得税优惠的小型微利企业标准,同时加大所得税优惠力度,提高增值税的起征点。
(2)结合材料,运用经济生活的有关知识,说明实施市场准入负面清单制度和减税措施是如何激发市场主体活力的。
(3)结合上述材料,运用矛盾的有关知识,分析说明对企业减税和国家税收收入增长之间的关系。
材料三:有人认为,我国实施市场准入负面清单制度和大规模减税措施,减少了政府对市场的干预,就是经济活动中的新自由主义。
(4)你赞同上述说法吗?请阐明你的理由。
学习贯彻党的十九大报告“转变政府职能,深化简政放权,创新监管方式”的要求,河北决心以更大力度,下好“放管服”改革“先手棋”,打好优化营商环境“攻坚战”,不断厚植新常态下发展新活力。简政放权的深化、服务方式的创新促进了营商环境的优化;越变越好的营商环境,又促进了改革红利持续释放,吸引更多企业和项目向河北聚集,全省经济发展迸发出新的活力。截至目前,河北出台改善营商环境的政策措施424项,改善内部工作流程154项,从制度层面固化营商环境整治成果。推行政府权力清单制度,促进权力公开透明运行。截至2018年10月底,全省市场主体总量达447.58万户,比“放管服”改革前增长了一倍。
结合材料,运用政治生活知识说明,在促进营商环境优化、提振企业发展信心的过程中河北省政府是如何作为的。
I was in the middle of the Amazon (亚马逊) with my wife, who was there as a medical researcher. We flew on a small plane to a faraway village. We did not speak the local language, did not know the customs, and more often than not, did not entirely recognize the food. We could not have felt more foreign.
We were raised on books and computers, highways and cell phones, but now we were living in a village without running water or electricity It was easy for us to go to sleep at the end of the day feeling a little misunderstood.
Then one perfect Amazonian evening, with monkeys calling from beyond the village green, we played soccer. I am not good at soccer, but that evening it was wonderful. Everyone knew the rules. We all spoke the same language of passes and shots. We understood one another perfectly. As darkness came over the field and the match ended, the goal keeper, Juan, walked over to me and said in a matter-of-fact way, “In your home, do you have a moon too?” I was surprised.
After I explained to Juan that yes, we did have a moon and yes, it was very similar to his, I felt a sort of awe (敬畏) at the possibilities that existed in his world. In Juan’s world, each village could have its own moon. In Juan’s world. the unknown and undiscovered was vast and marvelous. Anything was possible.
In our society, we know that Earth has only one moon. We have looked at our planet from every angle and found all of the wildest things left to find. I can, from my computer at home, pull up satellite images of Juan’s village. There are no more continents and no more moons to search for, little left to discover. At least it seems that way.
Yet, as I thought about Juan’s question, I was not sure how much more we could really rule out. I am, in part, an ant biologist, so my thoughts turned to what we know about insect life and I knew that much in the world of insects remains unknown. How much, though? How ignorant (无知的) are we? The question of what we know and do not know constantly bothered me.
I began collecting newspaper articles about new species, new monkey, new spider…, and on and on they appear. My drawer quickly filled. I began a second drawer for more general discoveries: new cave system discovered with dozens of nameless species, four hundred species of bacteria found in the human stomach. The second drawer began to fill and as it did I wondered whether there were bigger discoveries out there, not just species, but life that depends on things thought to be useless, life even without DNA. I started a third drawer for these big discoveries. It fills more slowly, but all the same, it fills.
In looking into the stories of biological discovery, I also began to find something else, a collection of scientists, usually brilliant occasionally half-mad, who made the discoveries. Those scientists very often see the same things that other scientists see, but they pay more attention to them, and they focus on them to the point of exhaustion (穷尽), and at the risk of the ridicule of their peers. In looking for the stories of discovery, I found the stories of these people and how their lives changed our view of the world.
We are repeatedly willing to imagine we have found most of what is left to discover. We used to think that insects were the smallest organisms (生物), and that nothing lived deeper than six hundred meters. Yet, when something new turns up, more often than not, we do not even know its name.
65. How did the author feel on his arrival in the Amazon?
A. Out of place. B. Full of joy. C. Sleepy. D. Regretful.
66. What made that Amazonian evening wonderful?
A. He learned more about the local language.
B. They had a nice conversation with each other.
C. They understood each other while playing.
D. He won the soccer game with the goal keeper.
67. Why was the author surprised at Juan’s question about the moon?
A. The question was too straightforward.
B. Juan knew so little about the world.
C. The author didn’t know how to answer.
D. The author didn’t think Juan was sincere.
68. What was the author’s initial purpose of collecting newspaper articles?
A. To sort out what we have known.
B. To deepen his research into Amazonians.
C. To improve his reputation as a biologist.
D. To learn more about local cultures.
69. How did those brilliant scientists make great discoveries?
A. They shifted their viewpoints frequently.
B. They followed other scientists closely.
C. They often criticized their fellow scientists.
D. They conducted in-depth and close studies.
70. What could be the most suitable title for the passage?
A. The Possible and the Impossible .
B. The Known and the Unknown .
C. The Civilized and the Uncivilized .
D. The Ignorant and the Intelligent.
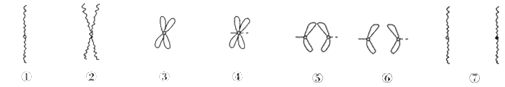
A. ①→②过程发生在有丝分裂间期,此时细胞内核膜解体、核仁消失
B. ④→⑤过程中染色单体的分开导致了染色体数目加倍
C. ⑤→⑥过程处于有丝分裂后期,细胞中的染色体移向细胞两极
D. ⑥→⑦过程中染色体解螺旋变为细丝状的染色质

(1)实验过程中,要保持____________________等环境条件与对照组相同且适宜;9:00时刻,一定光照强度下,叶肉细胞内02移动的方向是_________________。
(2)据图分析可知,在对小麦的各种处理中,___________处理不会导致植株出现“午休”现象,其原因可能是____________________________。
(3)图中光合速率的含义可表示为____________________,若用H2180浇灌,发现小麦叶肉细胞中出现了(CH2180),180转移途径是__________________________________________。
(4)为了进一步探究雾化处理对小麦叶片细胞呼吸是否有影响,请简单设计一个合理的实验方案________________________________。
请认真阅读下面短文,从短文后各题所给的A、B、C、D四个选项中,选出最佳选项。
Tess was a precocious(早熟) eight-year-old girl when she heard her Mom and Dad talking about her little brother, Andrew. 36 she knew was that he was very sick and they were completely 37 money. They were moving to an apartment complex next month because Daddy didn’t have the money for the doctor’s bills and their house. Only a(n) 38 could save him now.
Tess went to her bedroom and pulled a glass jelly(果冻) jar from its hiding place. She poured all the 39 out on the floor and counted carefully. Three times, even. The total had to be absolutely exact. No _40_ here for mistakes. After carefully placing the coins back in the jar, she slipped out of the back door, and 41 her way six blocks to a chemist’s.
She waited patiently for the pharmacist (药剂师) to give her some 42 , but he was too busy at this moment. Tess twisted her feet to make a noise. Nothing. She cleared her 43 with the most awful sound she could muster. No good.
Finally the pharmacist asked in an 44 tone of voice, “What do you want? I’m talking to my brother from Chicago 45 I haven’t seen in ages,” he said without waiting for a reply to his question.
“Well, I want to talk to you about my brother,” Tess answered back in the same annoyed tone. “His name is Andrew and he has something bad __46__ inside his head and my daddy says only a miracle can save him now. So how much does a miracle cost?”
“We don’t sell miracles here, little girl. I’m sorry, _47_ I can’t help you,” the pharmacist said, his voice _48_ a little.
There was a man there whose clothes were admirable. He asked the little girl, “What kind of a miracle does your brother need?”
“I don’t know” Tess replied with tears in her eyes. “I just know he' s _49_ sick and Mommy says he needs an operation. But my Daddy can’t pay _50_ it, so I want to use my money.”
“How much do you have?” asked the man. “One dollar and eleven cents,” Tess answered.
“A dollar and eleven cents — the _51_ price of a miracle for your little brother,” smiled the man, “Take me to _52_ you live. Let’s see if I have the kind of miracle you need.”
That well-dressed man was Dr. Carlton Armstrong, a surgeon, specializing in neurosurgery (神经外科). The operation was completely _53_ charge and it wasn’t long before Andrew was home again and did well.
Mom and Dad were happy but they wonder how much the operation would have _54_. Tess smiled. She knew exactly how much a miracle cost…one dollar and eleven cents…plus the _55_ of a little child.
| 36.A. As | B. All | C. All what | D. That |
| 37.A. in need | B. in short | C. out of | D. sort of |
| 38.A. miracle | B. doctor | C. God | D. operation |
| 39.A. change | B. jellies | C. candies | D. cookies |
| 40.A. way | B. doubt | C. chance | D. wonder |
| 41.A. drove | B. fought | C. made | D. struggled |
| 42.A. pills | B. attention | C. medicine | D. tablets |
| 43.A. mouth | B. eyes | C. ears | D. throat |
| 44.A. anxious | B. exciting | C. annoyed | D. tired |
| 45.A. who | B. where | C. because | D. which |
| 46.A. finding | B. planting | C. showing | D. growing |
| 47.A. and | B. or else | C. but | D. or |
| 48.A. soft | B. soften | C. softened | D. softening |
| 49.A. really | B. real | C. firm | D. firmly |
| 50.A. back | B. for | C. off | D. up |
| 51.A. actual | B. exact | C. average | D. true |
| 52.A. the place | B. the apartment | C. the complex | D. where |
| 53.A. free | B. free of | C. not | D. no |
| 54.A. spent | B. paid | C. cost | D . took |
| 55.A. thought | B. value | C. patience | D. faith |

A. 若a点pH=4,且c(Cl-)=m·c(ClO-),则Ka(HClO)=
B. 若x=100,b点对应溶液中:c(OH-)>c(H+),可用pH试纸测定其pH
C. b~c段,随NaOH溶液的滴入,
D. 若y=200,c点对应溶液中:c(OH-)-c(H+)=2c(Cl-)+c(HClO)
A. 气体的温度越高,分子平均动能越大
B. 晶体在物理性质上不一定表现出各向异性
C. 给自行车打气时越往下压,需要用的力越大,是因为分子间作用力表现为斥力引起的
D. 分子力表现为引力时,分子间的距离减小,则分子力可能减小
E. 空气的相对湿度越小,空气中水蒸气压强越接近同温度水的饱和汽压
A.去殖民化 B.政治中立
C.经济独立 D.区域集团化
A. 无产阶级登上历史舞台
B. 马克思主义在中国的传播
C. 中国
 的正确领导
的正确领导D. 新文化运动促进民众觉醒
高分子材料在生产生活中应用广泛。下列说法错误的是
A . 芦苇可用于制造黏胶纤维,其主要成分为纤维素
B . 聚氯乙烯通过加聚反应制得,可用于制作不粘锅的耐热涂层
C . 淀粉是相对分子质量可达几十万的天然高分子物质
D . 大豆蛋白纤维是一种可降解材料
A. 王权至高无上神圣不可侵犯
B. 法律保障了民主政治的发展
C. 法律为维护君主专制而创制
D. 法律的权威植根于历史传统

A. 奴隶贸易的兴起
B. 自由贸易政策的推行
C. 内燃机的应用
D. 垄断组织的形成

A. 水平力F的大小不变
B. 杆对小球A的支持力不变
C. 轻绳对小球B的拉力先变大后变小
D. 杆对小球A的摩擦力先变小后变大
材料一禁军一兵之费,以衣粮、特支、郊赉通计,一岁约费钱五十千;厢军一兵之费,岁约三十千。通一百一十八万余人,一岁约费四千八百万缗。此其大较也。
——摘编自(宋)蔡襄《养兵之费》
材料二(宋)真宗成平四年,有司言减天下冗吏十九万五千余人。所减者如此,未减者可知也……刘晏(唐朝人)以一千二百万贯供中原之兵而有余,令以三千六百万贯供川陕一军而不足。
——摘编自(清)赵翼《廿二史札记》
材料三臣谓宜令天下州郡,岁结群吏之课,必先疏其功过之状,则又以善恶深浅而相补除。第为三等,直云某人居某职事,能举其职,尝建立某功,事有利于民……其书过罚约此。凡郡县众吏,长吏亲书之,其守悴之成,则转运使、提点刑狱分校定之。逐部州郡设月日期套集,上于二司……伏望朝廷慎选才识之士,以授考功之职,益曾其员。
——摘编自(宋)张方平《刍荛论》
(1)根据材料一、二并结合所学知识,说明上述现象出现的原因。
(2)材料三的主张与同期哪场改革的核心观点类似?结合所学知识分析这场改革失败的原因。

A. 鹊桥质量
B. 月球质量
C. 地球质量
D. 鹊桥绕L2运转的速度
A.
【1】1992-2007年乌克兰耕地的变化标明这一时期该国
A. 人口数量减少 B. 城市化率提高 C. 土壤质量下降 D. 粮食单产提高
【2】1992-2007年乌克兰人均耕地增加最可能引起该国
A. 人均粮食产量增加 B. 农业生产投入增加
C. 粮食进口总量增加 D. 亩均农业产值增加
- 读下图,回答下列问题。 新疆区域示意图 (1)写出下列序号所代表的山脉和盆地的名称 ①
- 两个共点力的合力与分力的关系是A.合力大小一定等于两个分力大小之和B.合力大小一定大于两个分力大小之和C.合力大小一定小
- 生活中常常碰到涉及化学知识的某些问题,下列叙述正确的是( ) ①人的皮肤在强紫外线的照射下将会
- 在19世纪末的社会风尚转变过程中形成了阅报的风气,其中在维新思想传播方面影响最大的报纸是 A.《时务报》 B.
- 已知正比例函数反比例函数由构造一个新函数其图象如图(8)所示.(因其图象似双 钩,我们称之为“双钩函数”).给出下列几个
- 如图3所示.带电液滴从高h处自由落下,进入一个匀强电场与匀强磁场互相垂直的区域,磁场方向垂直纸面向里,电场强度为E,磁
- _______ the school, the village has aclinic, which was also
- 在图2-8-6所示电路的三根导线中,有一根是断的,电源,电阻R1、R2及另外两根导线都是完好的,为了查出断导线,某学生想
- 如图,有一块半圆形钢板,直径AB=20cm,计划将此钢板切割成下底为AB的等腰梯形,上底CD的端点在圆周上,且CD=10
- 若某物体做s=(1-t)2的直线运动,则其在t=1.2 s时的瞬时速度为________.
- I have no ideawhether the book is ________ great value to yo
- 如图,在平面直角坐标系中,已知,两点的坐标分别为,,是线段上一点(与,点不重合),抛物线()经过点,,顶点为,抛物线()
- TownCinema has__________ seats of all.A.mostcomfortable
- 如图所示,许多建筑采用玻璃进行外墙装潢,这在美化城市的同时却造成了光污染,造成这种污染的主要原因是由于阳光在玻璃表面发生
- From a college designed specifically for highschool students
- 已知:如图□ABCD中,DM=BN,BE=DF,求证:四边形MENF是平行四边形.
- 已知VmLAl2(SO4)3溶液中含有agAl3+,取出V/4 mL溶液稀释到4VmL,则稀释后溶液中的物质的量浓度为(
- Heseldom listens to others. He ________ answer for what he h
- 下列关于电源电动势的说法 ①电动势是用来比较电源将其它形式的能转化为电能本领大小的物理量 ②外电路断开时的路端电压等于电
- .清代地方行政制度大体沿袭明制,主管一省之民政、财政的官员,俗称“藩台”。该官职的正式名称是 A.节度使



